BLOG
Difference between Outer and Inner Rotor of Coreless Generator
A coreless generator is a common type of permanent magnet generator that is commonly used in applications such as wind and hydroelectric power generation. Coreless generators can be categorized into two main types: external rotor and internal rotor, each of which has its own characteristics in terms of structure and performance.
Difference between External Rotor and Internal Generator
1. Structural Design
Outer Rotor (Outer Rotor):
Rotor outside, stator inside: In the design of the outer rotor, the permanent magnets are mounted on the outer circumference of the rotor, and the rotor is wrapped around the outside of the stator.
Large diameter design: The diameter of the outer rotor is usually larger, which helps to increase the torque of the generator.
Stability and cooling: Since the rotor is on the outside, heat dissipation is better and mechanical stability is higher for high speed applications.
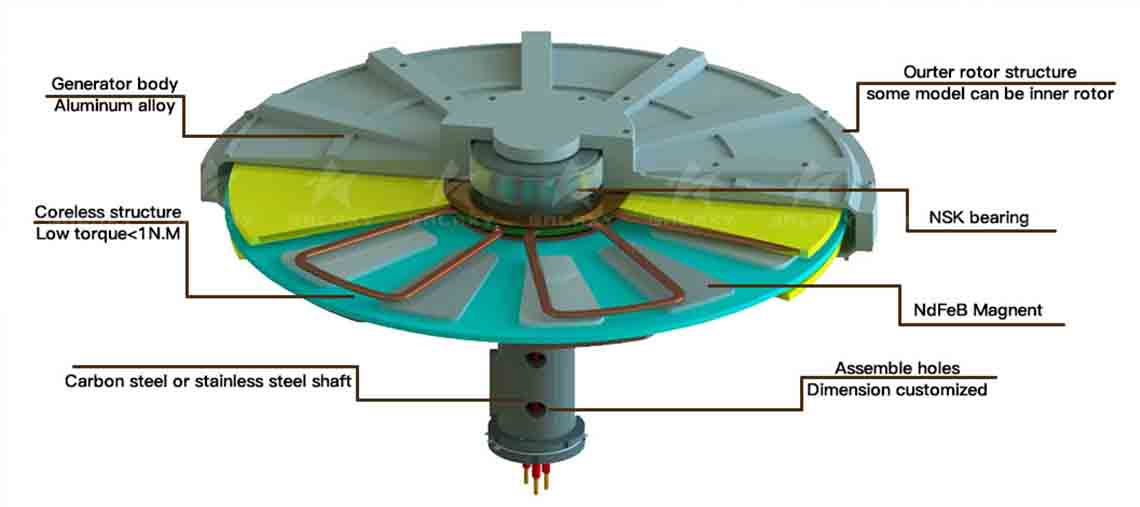
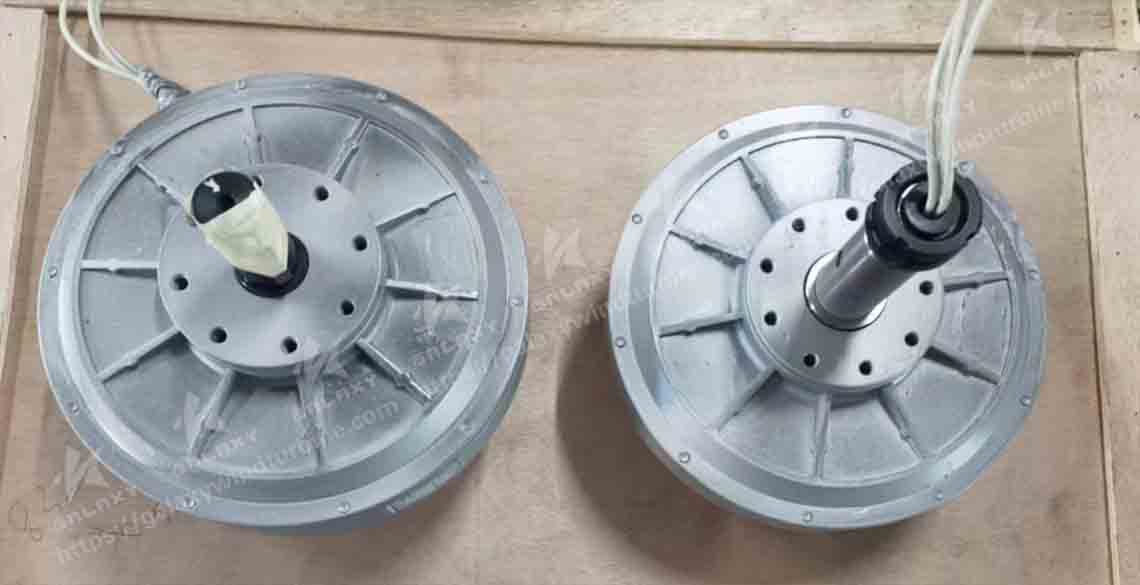
Inner Rotor (Inner Rotor):
Rotor inside, stator outside: In the Inner Rotor design, the permanent magnets are mounted on the inner circumference of the rotor and the stator is wrapped around the outside of the rotor.
Compact design: The Inner Rotor is more compact and suitable for applications where space is limited.
Maintenance and Cooling: With the rotor inside, the cooling effect may be slightly worse and better cooling measures are required.

2. Torque and Efficiency
External Rotor:
Higher starting torque: Due to the larger radius of the outer rotor, higher starting torque is provided, suitable for low-speed, high-torque applications such as wind power generation.
Better heat dissipation: the rotor is located on the outside and is in direct contact with the air, which dissipates heat better, contributing to higher efficiency and longer life.
Inner Rotor:
Higher running speed: the inner rotor is suitable for high speed and low torque applications, such as some small power tools or electric vehicles, due to its compact design.
Higher efficiency: the compact design of the inner rotor results in lower energy loss, but requires a good cooling system to maintain efficient operation.
3. Application Scenarios
Outer Rotor:
Wind power: External rotor coreless PMGs are commonly used for wind power generation and are well suited for wind power systems due to their high starting torque and better heat dissipation.
Industrial use: The high stability and efficiency of the outer rotor design makes it widely used in some industrial applications as well.
Inner Rotor:
Electric Vehicles: Inner rotor coreless PMGs are widely used in electric vehicles and some small power tools due to their compactness and high efficiency characteristics.
Portable equipment: It is suitable for some portable equipments that require high rotational speed and have limited space.

Summary
External rotor and internal rotor coreless PMGs have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type to use depends mainly on the specific application requirements. The external rotor is suitable for high torque and high heat dissipation requirements, while the internal rotor is suitable for compact and high speed applications.